BSH201 - Logic level P-channel enhancement mode Field-Effect Transistor (FET) in a plastic package using vertical D-MOS technology. This product is designed and qualified for use in computing. Find your mosfet transistor easily amongst the 51 products from the leading brands (Littelfuse, ROHM Semiconductor, Infineon.) on DirectIndustry, the industry specialist for your professional. VRF151, VRF151 Datasheet, VRF151 PDF, N-CHANNEL RF POWER VERTICAL MOSFET.
Trench MOSFET basics | What is Trench MOSFET
This page covers Trench MOSFET basics and mentions Trench MOSFET construction. The links to MOSFET and comparison between MOSFET and other transistor types are also mentioned.
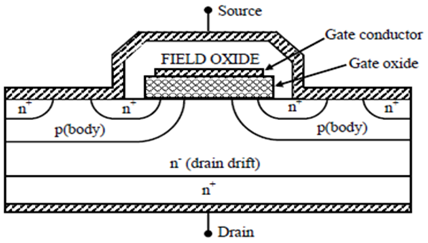
Vertical Mosfet Structure
The device trench gate MOSFET has lowest ON state resistance among all the variants of MOS devices.Hence it is considered as most suitable power device for low to medium voltage power applications.
The architecture is designed such that it conducts the current vertically from one surface to the othersurface. Due to this the trench MOSFET achieves high drive capability.It is realized by packing millions of trenches on a chip, deepenough to cross the oppositely doped 'body' region below the top surface. Eachtrench houses a gate dielectric and gate electrode to control the current conductionin its vicinity by the virtue of field effect.
Trench MOSFET Construction

Similar to any other MOSFET, a trench MOSFET cell contains the drain, gate, source, body andthe channel regions but exhibits a vertical direction of current flow. All the cellsare connected to work in parallel in order to reduce the value of RON.Figure depicts basic device structure for trench MOSFET.Trench MOSFETs are mainly used for less than 200 voltage rating due totheir higher channel density and thus lower on-resistance.
The amount of current trench MOSFET conducts depends on the on-resistance of the MOSFET which is expressed asfollows.
RDSON = VD/ID
Vertical Jfet
For a trench MOSFET, RDSON consists of the following components which is depictedin the figure-2:
• RS: source resistance
• RCH: channel resistance
• RACC: resistance from the accumulation region
• REPI: resistance from the top layer of silicon(epitaxial silicon, also known as epi); epi controls the amount of blocking voltage the MOSFET can sustain.
• RSUBS: resistance from the silicon substrate on which the epi is grown
MOSFET and BJT related links
PNP Transistor Vs NPN Transistor➤
BJT vs FET➤
JUGFET vs MOSFET➤
Depletion MOSFET vs Enhancement MOSFET➤
MOSFET Fabrication Technology➤
MOSFET vs BJT-Difference between MOSFET and BJT➤
Application Note-MOSFET as switch and amplifier➤
Difference between NMOS vs PMOS➤
What is Difference between
difference between FDM and OFDM
Difference between SC-FDMA and OFDM
Difference between SISO and MIMO
Difference between TDD and FDD
Difference between 802.11 standards viz.11-a,11-b,11-g and 11-n
OFDM vs OFDMA
CDMA vs GSM
RF and Wireless Terminologies

Share this page
Vertical Mosfet Structure
Vertical Mosfet Dimensions
Translate this page

